Bladder cancer is a condition where abnormal cells multiply uncontrollably in the bladder lining. Detecting bladder cancer typically involves several diagnostic steps, followed by tailored treatment options depending on the stage and type of cancer.
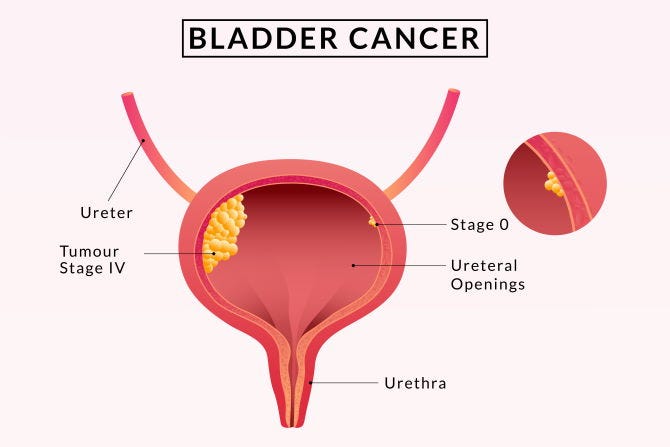
Detection of Bladder Cancer
Symptoms and Initial Screening:
- Blood in Urine (Hematuria): This is the most common symptom. Visible blood or blood detected under a microscope during a urinalysis may indicate bladder cancer.
- Urinary Changes: Frequent urination, pain during urination, or urgency can also be signs, though these are less specific.
Diagnostic Tests:
- Cystoscopy: A thin, flexible tube (cystoscope) is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to visually inspect the bladder lining for abnormalities.
- Biopsy: If suspicious areas are found during cystoscopy, a small sample of tissue (biopsy) may be taken for examination under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
Imaging Tests:
- CT Scan or MRI: These imaging tests help determine the extent of cancer spread (staging) beyond the bladder.
Treatment Options for Bladder Cancer
Treatment options for bladder cancer depend on several factors, including the stage of cancer, overall health, and personal preferences.
Non-Invasive or Early Stage Bladder Cancer:
- Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): For tumors confined to the inner layers of the bladder, this procedure involves removing the tumor through a cystoscope.
- Intravesical Therapy: After TURBT, medications (chemotherapy or immunotherapy) can be delivered directly into the bladder to destroy remaining cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Muscle-Invasive or Advanced Bladder Cancer:
- Surgery: Partial or radical cystectomy may be necessary to remove part or all of the bladder. In some cases, nearby lymph nodes may also be removed.
- Chemotherapy: Used before or after surgery (neoadjuvant or adjuvant), or as the primary treatment for advanced cancer that has spread beyond the bladder.
- Radiation Therapy: Sometimes used instead of surgery, or in combination with chemotherapy, especially for cancers that cannot be surgically removed.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy:
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that specifically target cancer cells based on their genetic characteristics.
- Immunotherapy: Drugs that help the immune system recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
Follow-Up Care:
- After treatment, regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor for recurrence and manage any side effects from treatment.
Conclusion
Early detection of bladder cancer is crucial for successful treatment outcomes. Advances in diagnostic techniques and treatment options continue to improve the prognosis for individuals diagnosed with bladder cancer. Tailored treatment plans, often involving a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and supportive care, aim to achieve the best possible outcomes while preserving bladder function and quality of life.
Comments
Post a Comment