Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a condition characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function over time. Early diagnosis and proper staging are crucial for managing CKD effectively and preventing complications such as kidney failure.
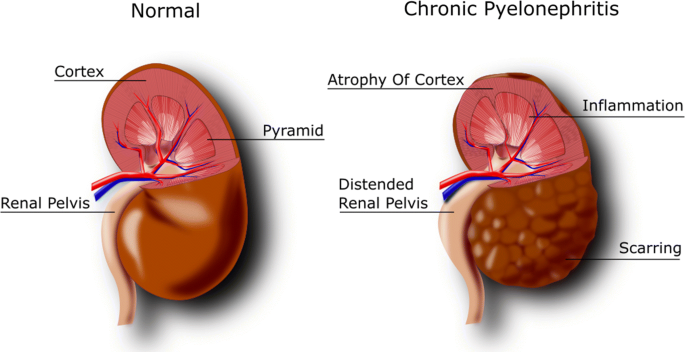
Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD):
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
- A healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history to assess risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, family history of kidney disease, and exposure to nephrotoxic substances. A physical examination may reveal signs of fluid retention or hypertension.
2. Laboratory Tests:
- Serum Creatinine and Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR): Creatinine is a waste product generated by muscle metabolism and excreted by the kidneys. Elevated serum creatinine levels indicate reduced kidney function. eGFR is calculated using serum creatinine, age, sex, and race to estimate kidney function.
- Urinalysis: Analysis of a urine sample can detect abnormalities such as proteinuria (presence of excess protein), hematuria (blood in urine), and urinary sediment indicative of kidney damage.
3. Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the kidneys may be performed to assess their size, shape, and structure. It can help detect structural abnormalities or obstruction.
- CT Scan or MRI: These imaging techniques provide detailed images of the kidneys and surrounding structures, useful for evaluating kidney anatomy and detecting abnormalities.
4. Kidney Biopsy (if necessary):
- In certain cases where the cause of CKD is unclear or to assess the severity of kidney damage, a kidney biopsy may be performed. A small tissue sample is taken for microscopic examination.
Staging of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD):
CKD is staged based on the level of kidney function (eGFR) and the presence of kidney damage, as determined by laboratory tests and imaging studies. The staging system commonly used is from the National Kidney Foundation:
Stage 1: Kidney Damage with Normal or High eGFR (≥90 mL/min/1.73 m²):
- Persistent proteinuria (protein in urine) or other markers of kidney damage are present, but eGFR is normal or only slightly reduced.
Stage 2: Mildly Reduced eGFR (60–89 mL/min/1.73 m²):
- Evidence of kidney damage with mildly reduced kidney function.
Stage 3: Moderately Reduced eGFR (30–59 mL/min/1.73 m²):
- Kidney function is moderately decreased, indicating moderate CKD. This stage is further divided into:
- Stage 3a: eGFR 45–59 mL/min/1.73 m²
- Stage 3b: eGFR 30–44 mL/min/1.73 m²
Stage 4: Severely Reduced eGFR (15–29 mL/min/1.73 m²):
- Kidney function is significantly reduced, indicating severe CKD. At this stage, preparation for kidney replacement therapy (dialysis or transplant) may be initiated.
Stage 5: Kidney Failure (eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m²):
- Also known as end-stage renal disease (ESRD), kidney function is severely impaired, and the kidneys are unable to maintain life-sustaining functions without dialysis or kidney transplantation.
Monitoring and Management:
- Regular Monitoring: Patients with CKD require regular monitoring of kidney function, blood pressure, urine protein levels, and other parameters to assess disease progression and adjust treatment.
- Management: Treatment focuses on addressing underlying causes, managing complications, and slowing the progression of CKD through lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise), medications (blood pressure control, diabetes management), and sometimes renal replacement therapy (dialysis or transplantation).
Early detection and intervention can help preserve kidney function and improve outcomes for individuals living with chronic kidney disease. Patients should work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan based on their stage of CKD and individual health needs.
Comments
Post a Comment