Understanding the Types of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are solid mineral and salt deposits that form within the kidneys or urinary tract. These stones can vary in size, shape, and composition, and their development can be influenced by a variety of factors including diet, hydration levels, and underlying medical conditions.
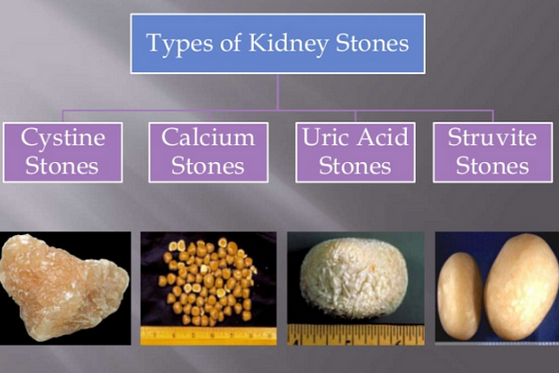
Understanding the different types of kidney stones is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
1. Calcium Stones
Calcium stones are the most common type of kidney stones, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. These stones are primarily composed of calcium oxalate or calcium phosphate. Oxalate is naturally found in many foods and is also produced by the liver. When the concentration of oxalate in the urine is high and combines with calcium, it can form crystals that eventually develop into stones. Factors such as a high-oxalate diet, certain medical conditions, and genetic factors can increase the risk of calcium stone formation.
2. Uric Acid Stones
Uric acid stones form when there is an excessive accumulation of uric acid in the urine. Uric acid is a waste product resulting from the breakdown of purines, substances found in certain foods and also produced by the body. Individuals with conditions such as gout, which is characterized by high levels of uric acid in the blood, are at an increased risk of developing uric acid stones. These stones can also occur in people who have undergone chemotherapy or have a history of dehydration.
3. Struvite Stones
Struvite stones, also known as infection stones, form in response to urinary tract infections caused by certain bacteria, such as Proteus or Klebsiella species. These bacteria produce urease, an enzyme that breaks down urea in urine into ammonium, which raises the pH of the urine. This alkaline environment promotes the formation of struvite crystals, which can grow rapidly into large stones. Struvite stones often fill the renal pelvis and can cause significant obstruction and kidney damage if not treated promptly.
4. Cystine Stones
Cystine stones are rare and typically hereditary. They form as a result of a genetic disorder known as cystinuria, which causes abnormal reabsorption of cystine, an amino acid, in the kidneys. As a result, cystine levels in the urine become excessively high, leading to the formation of cystine crystals that can aggregate and form stones. Cystine stones are often large and difficult to treat, requiring specialized interventions such as medication to reduce cystine levels or surgical removal.
5. Other Stones
In addition to the main types mentioned above, other less common types of kidney stones include:
- Calcium phosphate stones: These stones are composed primarily of calcium phosphate and may form in individuals with metabolic disorders or certain medical conditions.
- Drug-induced stones: Certain medications, such as protease inhibitors used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, can increase the risk of kidney stone formation.
- Mixed stones: Some kidney stones may have a combination of minerals, making them more challenging to classify and treat.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of kidney stones is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Treatment strategies may vary depending on the type of stone, its size, location, and underlying risk factors. Lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, medication, and surgical interventions are all potential options for managing kidney stones and preventing their recurrence.
If you suspect you have kidney stones or experience symptoms such as severe pain, blood in the urine, or difficulty urinating, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly for proper evaluation and treatment.
Comments
Post a Comment